Holistic Health Benefits of the Milk Matrix: Beyond Individual Nutrients For many years, nutrition research focused on how individual nutrients,..
GET THE FACTSDisease Prevention
Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer. One cup of milk contains 15 essential nutrients, which contribute to a nutritious balanced diet. Read on to learn more about the role milk can play in your patients’ diets to aid in disease prevention.
HYPERTENSION
In Canada, 23% of adults report that they have been diagnosed with hypertension by a health-care professional or take anti-hypertensive medication.1 In addition to medication, there are lifestyle interventions, such as changes in dietary patterns, which can help manage high blood pressure.
Milk is part of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) plan, which is an evidence-based eating pattern to help lower blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of developing heart disease.2 The combination of foods in the DASH eating pattern can decrease systolic blood pressure by about 6 to 11 mm Hg in both hypertensive and normotensive people.3
The DASH eating pattern is rich in:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Milk and milk products
- Whole grains
- Fish, poultry, beans, seeds, and nuts.4
It’s also lower in salt, sugar, fat and red meat compared to the typical North American diet.
The DASH eating pattern includes two to three servings of low-fat milk or milk products daily.5One serving is equal to a cup of milk or yogurt, or 1.5 ounces of cheese.6Milk is an important part of DASH because it’s a source of protein, and contains minerals including calcium, potassium and magnesium, which help lower blood pressure levels.
While the original DASH studies focused on low-fat milk as part of the eating pattern, a 2016 study found that a higher-fat DASH eating pattern (replacing low-fat milk products with full-fat milk products) was able to lower blood pressure as much as the standard DASH eating pattern.7Using higher fat milk products also lowered triglyceride levels and did not adversely impact blood cholesterol levels.
HEART HEALTH AND TYPE 2 DIABETES
According to the Heart & Stroke Foundation, nine in 10 Canadians have at least one risk factor for heart conditions, stroke or vascular cognitive impairment.8Research shows that some dietary patterns can help reduce heart disease risk.
Both the DASH and the Mediterranean eating patterns include nourishing whole foods that help reduce heart disease risk.9 The Mediterranean eating pattern includes:
- Whole grains
- Fruits and vegetables
- Beans and nuts
- Herbs and spices
- Healthy fats such as olive oil
- Fish and seafood
- Dairy
- Eggs and poultry10
In this pattern, red meats and sweets are eaten sparingly.
In addition to protecting heart health, a systematic review and meta-analysis found that the Mediterranean eating pattern is associated with better glycaemic control compared to a low-fat diet, which suggest that it is suitable for managing type 2 diabetes.11
This is important information for the 29 percent of Canadians who live with diabetes or prediabetes, and the 10 percent who live with diagnosed diabetes.12
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition looked at the effect of a Mediterranean eating pattern supplemented with dairy foods to see the impact on cardiovascular risk factors.13 The randomized, controlled study compared a Mediterranean eating patternwith 3–4 daily servings of dairy to a low-fat diet for eight weeks.
The researchers found that the Mediterranean eating pattern with dairy resulted in significantly lower blood pressure, higher HDL “good” cholesterol, and lower triglycerides compared to the low-fat diet. They concluded that the Mediterranean eating pattern with dairy was “appropriate for an improvement in cardiovascular risk factors in a population at risk of cardiovascular disease.”14
MILK AND COLORECTAL CANCER
A recent study published in the Lancet says that colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide.15 The American Institute for Cancer Research reports that there is strong evidence that dairy products decrease the risk of colorectal cancer.16
Clinical studies have highlighted an association between dairy product consumption and a decreased risk of colorectal cancer. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis found consistent significant decrease in the risk of colorectal cancer in those who consumed more dairy products including milk and cheese.17
Specifically, the study found that:
- High consumption of total dairy products and total milk was associated with a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer at any anatomic location, including the proximal and distal colon and the rectum.
- Low-fat milk consumption was associated with a lower risk of colon cancer specifically
- Cheese consumption was associated with the prevention of proximal colon cancer
OSTEOPOROSIS
Many of the nutrients found in milk, such as protein and calcium, are important for bone health. Having milk and dairy products as part of meals and snacks is beneficial for every age group but especially for children and adolescents, when bones are rapidly developing.18
Osteoporosis is a bone disease (low bone mass), which can lead to an increased risk of fractures.19 According to Osteoporosis Canada, this disease aects about two million Canadians.20 The National Osteoporosis Foundation position statement says, “there is strong evidence for calcium (Grade A) and good evidence (Grade B) for dairy products and vitamin D in peak bone mass development, a key predictor of fractures.”21
Studies on the association between intake of dairy products and the risk for osteoporotic fractures have shown that higher long-term consumption of dairy foods is associated with a lower risk of hip fractures.22 Another recent study shows that providing more milk and dairy foods to long-term care residents can help reduce the risk of falls and fractures.23 In the study, dairy food intake increased from 2.0 to 3.5 servings daily, and the risk of fractures from falls decreased by 33 percent.
The association between milk and bone health is not fully understood, but researchers believe it is due to a number of nutrients in dairy that work synergistically to support bones. These nutrients include calcium, protein, potassium, magnesium, vitamin D, zinc and phosphorus. Milk contains more of these key nutrients per calorie compared to any other foods.24
CITATIONS
1 Statistics Canada https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/82-625-x/2021001/article/00001-eng.html
2 US National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Guide to Lowering your blood pressure with DASH https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/public/heart/dash_brief.pdf
3 Challa, H. DASH Diet to Stop Hypertension. May 2021. (book) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482514/
4 US National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Guide to Lowering your blood pressure with DASH https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/public/heart/dash_brief.pdf
5 US National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Following the Dash Eating Plan https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/education/dash/following-dash
6 US National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Following the Dash Eating Plan https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/education/dash/following-dash
7 Chiu S et al. (2016). Comparison of the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet and a higher-fat DASH diet on blood pressure and lipids and lipoproteins: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 103:341-347 doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.123281
8 Heart & Stroke. Connected by the Numbers https://www.heartandstroke.ca/articles/connected-by-the-numbers
9 Mediterranean Diet. Oldways https://oldwayspt.org/traditional-diets/mediterranean-diet
10 ibid
11 Esposito K et al. (2015). A journey into a Mediterranean diet and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with meta-analyses. BMJ Open. 5(8):e008222 dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008222
12 Diabetes in Canada https://www.diabetes.ca/DiabetesCanadaWebsite/media/Advocacy-and-Policy/Backgrounder/2021_Backgrounder_Canada_English_FINAL.pdf
13 Wade A et al. (2018). Mediterranean diet supplemented with dairy foods improves markers of cardiovascular risk: results from the MedDairy randomized controlled trial The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 108(6):1166–1182 doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqy207
14 ibid
15 Sharma R et al. (2019). Global, regional, and national burden of colorectal cancer and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2022;0(0) doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00044-9
16 American Institute for Cancer Research. Meat, Fish & Dairy https://www.aicr.org/research/the-continuous-update-project/meat-fish-dairy/
Resources
Milk and Mucus
Milk and Mucus The current body of research indicates that milk and other dairy foods do not increase mucus production...
GET THE FACTSMilk and Pediatric Nutrition
MILK AND PEDIATRIC NUTRITION Growing Strong: The Importance of Milk to Nourish Children Leading pediatric and health organizations recognize the..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Physical Activity
Milk and Physical Activity Whether your patients are occasional gym-goers or are training intensely for a triathlon or sport tournament,..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Lactose Intolerance
Milk and Lactose Intolerance Having lactose intolerance does not mean your patients need to give up dairy Highlights: Evidence shows..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Hypertension
MILK AND BLOOD PRESSURE Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease and hypertension...
GET THE FACTSDairy and Colorectal Cancer
DAIRY AND COLORECTAL CANCER Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men and the third in..
GET THE FACTSHeart Health Benefits Of Milk
Heart Health Benefits Of Milk Diet and lifestyle play a role in heart disease prevention. It is estimated that 80%..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Plant Based Drinks
MILK AND PLANT BASED DRINKS There are many different plant-based beverages (PBB) available in the grocery store and it is..
GET THE FACTSDisease Prevention
Disease Prevention Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes..
GET THE FACTSMilk Nutrition Facts
Milk Nutritions Facts Milk is a source of essential nutrients. There is extensive evidence to show that including milk and..
GET THE FACTSRESOURCES
Download useful resources, research studies, and fact sheets on the benefits of dairy

Nutrients in Dairy
As a source of complete protein and essential nutrients, drinking milk is a simple way to support optimal health.
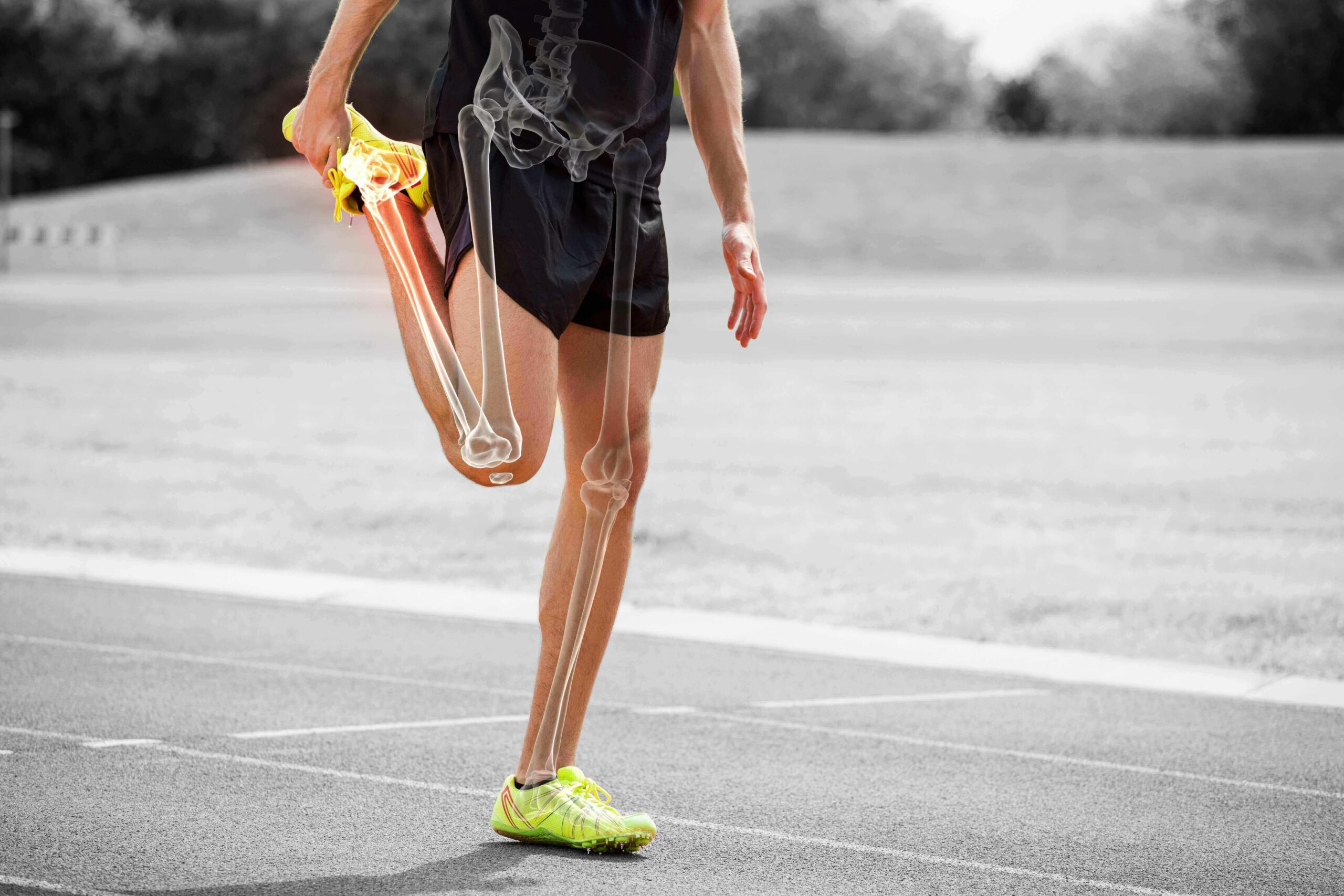

Dairy and Disease Prevention
Naturally nutrient dense, milk helps to combat nutrition deficiencies and ward off heart disease, hypertension, and colorectal cancer.

Dairy Milk and Plant Based Beverages
All forms of milk, including lactose-free milk, contain complete protein, vitamins, and minerals.

Heart Health Benefits of Milk
It is estimated that 80% of heart disease cases can be prevented with lifestyle changes that include a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.

Dairy and Colorectal Cancer
Studies have shown that high consumption of total dairy products and total milk was associated with a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer.

Milk and Hypertension
Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease and hypertension. Learn how adding milk into your patients’ diets can help with blood pressure management.

Milk and Lactose Intolerance
Some people have trouble digesting lactose, but that doesn’t mean giving up dairy! Read on to learn more about lactose intolerance, how it’s formally diagnosed, and how you can provide the best nutrition advice to patients.

Milk and Physical Activity
Milk has a unique combination of nutrients that make it the ideal beverage for post-exercise rehydration and protein synthesis.

Milk and Pediatric Nutrition
Leading pediatric and health organizations recognize the benefits of milk and dairy foods for early childhood. Just how much milk is recommended for children, and which nutrients will kids get from a tall glass of milk?

Milk and Mucus
When a runny nose or congestion appears, many people believe they need to cut out milk to reduce mucus. It turns out that this is a myth, and studies show that milk does not cause mucus.
Diabetes Prevention and Milk
Take a closer look at the role of milk in the prevention of T2D. There are potential mechanisms through which milk and dairy foods may play a role in reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes





