Holistic Health Benefits of the Milk Matrix: Beyond Individual Nutrients For many years, nutrition research focused on how individual nutrients,..
GET THE FACTSThe Dairy Matrix
Milk, cheese and yogurt contain many essential nutrients, including protein, calcium and magnesium. It’s increasingly recognized that these individual nutrients work together synergistically and interact in unique ways, which is the reason for their overall beneficial effects on health for people of all ages. In addition, the process of dairy fermentation, for foods like yogurt and cheese, also add to the health benefits. Together, these attributes are known as the dairy matrix.
All about the matrix
Historically, traditional nutrition research focused on one nutrient at a time. Now researchers are also interested in the complex interactions between nutrients, or the matrix1. Since people don’t eat individual foods or nutrients in isolation — they eat foods grouped together into meals — research that focuses on matrices is more important than focusing on any single nutrient.
Researchers define a ‘food matrix’ as “a function of both a food’s structure and its nutrient composition, and how these nutrients interact with each other.”2 In the case of dairy foods, it explains how protein, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates and fat work together to provide nutritional benefits, and how fermentation also plays a role (in the case of cheese and yogurt).
Benefits from the dairy matrix
Some nutrients are easier to digest when processed in a certain way. For example, when yogurt or cheese are fermented with bacteria, lactose sugar is broken down. This makes them easier to digest for people with lactose intolerance3.
Certain nutrients also work together to help reduce disease risk. For example, studies show that dairy foods reduce colon cancer risk4. Researchers say that this is due to a combination of factors, including:
- Calcium and vitamin D, which protect colon cells
- Fermentation, which produces short-chain fatty acids that protect the colon5.
Consider this: when nutrients are looked at in isolation, it’s common to hear claims like “dairy is high in saturated fat.” One nutrient becomes the enemy, which doesn’t account for the fact that:
- Dairy is high in beneficial protein, vitamins and minerals
- Some saturated fatty acids have health benefits6
The overall health benefits of a food are more complex than just looking at one nutrient; that’s why the dairy matrix is important to consider as a whole.
Despite containing some saturated fat, dairy foods have not been shown to produce the negative health effects one would suspect. In fact, the opposite is true, thanks to the sum of the dairy matrix.
- Research shows benefit for dairy foods on reducing hypertension and protecting heart health7. The interaction of calcium, phosphorus, the milkfat globule membrane, and starter cultures from fermentation (the dairy matrix) can work synergistically to modify saturated fatty acid-induced increases in blood lipids8.
- A meta-analysis on dairy and heart health showed that eating dairy foods had favorable or neutral associations with cardiovascular health9.
- A 2022 study showed that enjoying up to 200 grams of dairy foods daily had no detrimental effect on heart health, and fermented cheese and yogurt were associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular events10
Studies also highlight the special role of dairy foods on bone health, which can also be attributed to the dairy matrix. In addition to calcium, there are other nutrients in dairy foods that work synergistically to build strong bones. These include:
- Protein
- Vitamin D
- Phosphorus
- Magnesium
- Bacteria (in fermented dairy)11,12
The bottom line? When it comes to nutrition, we have to consider the bigger picture. Foods aren’t eaten in isolation. And certainly, the health effects of dairy foods extend beyond their individual parts. Researchers will continue to explore the dairy matrix to see how the unique nutrient composition of dairy foods can provide a variety of significant health benefits.
CITATIONS
1https://www.bmj.com/content/361/bmj.k2392
2Thorning TK, et al. (2017). Whole dairy matrix or single nutrients in assessment of health effects: current evidence and knowledge gaps. Am J Clin Nutr. 105(5):1033-1045. doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.151548
3Canadian Society of Intestinal Research. Lactose Intolerance. https://badgut.org/information-centre/a-z-digestive-topics/lactose-intolerance/
4Barrubés L, et al. (2019). Association Between Dairy Product Consumption and Colorectal Cancer Risk in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiologic Studies. Adv Nutr. 10(suppl_2):S190-S211. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy114.
5Weaver, C. (2021). Dairy matrix: is the whole greater than the sum of the parts?, Nutrition Reviews, Volume 79, Issue Supplement_2, https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuab081
6Dehghan M, et al. (2017). Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 390(10107):2050-2062. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32252-3
7Giosuè A, et al. (2022). Consumption of Dairy Foods and Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2022;14(4):831. doi:10.3390/nu14040831
8International Dairy Federation. The importance of the dairy (food) matrix in the evaluation of the nutritional quality and health effects of food. https://t8543074.p.clickup-attachments.com/t8543074/0490e8cc-e330-4316-befd-2a81f913e42e/IDF_Fact%20Sheet.pdf?view=open
9https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2161831322007876?via%3Dihub
10https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/4/831
11https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8072827/
12https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3330619/#:~:text=Nutritional%20needs%20for%20bone%20health,also%20important%20for%20bone%20health
Resources
Milk and Mucus
Milk and Mucus The current body of research indicates that milk and other dairy foods do not increase mucus production...
GET THE FACTSMilk and Pediatric Nutrition
MILK AND PEDIATRIC NUTRITION Growing Strong: The Importance of Milk to Nourish Children Leading pediatric and health organizations recognize the..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Physical Activity
Milk and Physical Activity Whether your patients are occasional gym-goers or are training intensely for a triathlon or sport tournament,..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Lactose Intolerance
Milk and Lactose Intolerance Having lactose intolerance does not mean your patients need to give up dairy Highlights: Evidence shows..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Hypertension
MILK AND BLOOD PRESSURE Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease and hypertension...
GET THE FACTSDairy and Colorectal Cancer
DAIRY AND COLORECTAL CANCER Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men and the third in..
GET THE FACTSHeart Health Benefits Of Milk
Heart Health Benefits Of Milk Diet and lifestyle play a role in heart disease prevention. It is estimated that 80%..
GET THE FACTSMilk and Plant Based Drinks
MILK AND PLANT BASED DRINKS There are many different plant-based beverages (PBB) available in the grocery store and it is..
GET THE FACTSDisease Prevention
Disease Prevention Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes..
GET THE FACTSMilk Nutrition Facts
Milk Nutritions Facts Milk is a source of essential nutrients. There is extensive evidence to show that including milk and..
GET THE FACTSRESOURCES
Download useful resources, research studies, and fact sheets on the benefits of dairy

Nutrients in Dairy
As a source of complete protein and essential nutrients, drinking milk is a simple way to support optimal health.

Dairy and Disease Prevention
Naturally nutrient dense, milk helps to combat nutrition deficiencies and ward off heart disease, hypertension, and colorectal cancer.

Dairy Milk and Plant Based Beverages
All forms of milk, including lactose-free milk, contain complete protein, vitamins, and minerals.

Heart Health Benefits of Milk
It is estimated that 80% of heart disease cases can be prevented with lifestyle changes that include a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.

Dairy and Colorectal Cancer
Studies have shown that high consumption of total dairy products and total milk was associated with a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer.

Milk and Hypertension
Milk plays a role in disease prevention for many chronic conditions, including heart disease and hypertension. Learn how adding milk into your patients’ diets can help with blood pressure management.

Milk and Lactose Intolerance
Some people have trouble digesting lactose, but that doesn’t mean giving up dairy! Read on to learn more about lactose intolerance, how it’s formally diagnosed, and how you can provide the best nutrition advice to patients.

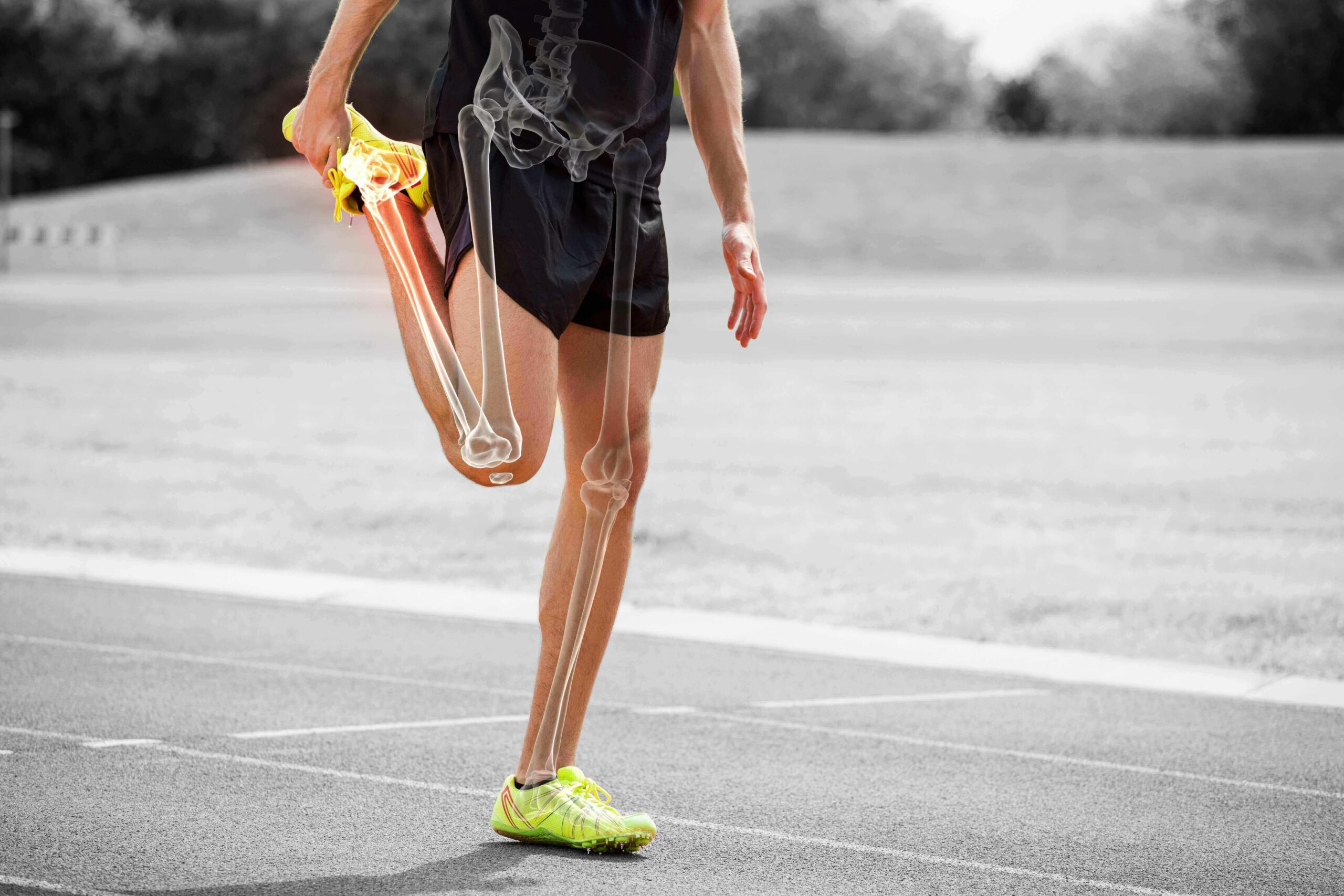
Milk and Physical Activity
Milk has a unique combination of nutrients that make it the ideal beverage for post-exercise rehydration and protein synthesis.

Milk and Pediatric Nutrition
Leading pediatric and health organizations recognize the benefits of milk and dairy foods for early childhood. Just how much milk is recommended for children, and which nutrients will kids get from a tall glass of milk?

Milk and Mucus
When a runny nose or congestion appears, many people believe they need to cut out milk to reduce mucus. It turns out that this is a myth, and studies show that milk does not cause mucus.
Diabetes Prevention and Milk
Take a closer look at the role of milk in the prevention of T2D. There are potential mechanisms through which milk and dairy foods may play a role in reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes





